×
![Enlarged Image]()
Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME)
Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS)
Overview
Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) is a method of sampling a model input space, usually for obtaining data for training metamodels or for uncertainty analysis. LHS typically requires less samples and converges faster than Monte Carlo Simple Random Sampling (MCSRS) methods when used in uncertainty analysis. By representing each variable as its Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) (prior distribution) and partitioning the CDF into N regions and taking a single sample from each region, this increases the likelihood that the full range of the posterior distribution is sampled. Once a suitable CDF sample is made, the sample CDF value is inversely mapped back to a parameter valueA requirement for LHS is that each region of the CDF can only be sampled once for each parameter. This is best visualized in a 2D space with the following figure:
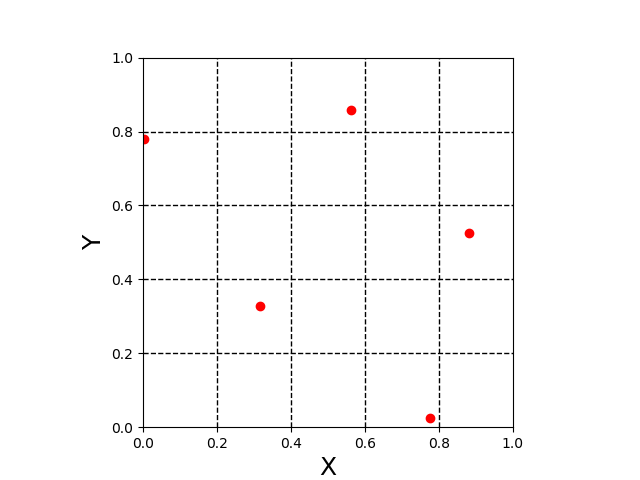
Fig 1. Example 2D LHS sample.
As seen in Figure 1, there is only one sample in each row and column in (X,Y) space. Due to the possibility of clustering (LHS sample with points close together) of sample points, a nearest neighbor restriction can be imposed.
Posterior Distribution - the resulting statistical distribution of the model output
Converting LHS output from Standard Uniform to Parameter Space
Terminology
Prior Distribution - the statistical distribution of the input parameters to a modelPosterior Distribution - the resulting statistical distribution of the model output
Python Implementation
An example implementation of a LHS algorithm is below. This code outputs samples for the standard uniform and standard normal distributions. Each random sample can be converted to parameter values via the following equations:Converting LHS output from Standard Uniform to Parameter Space
x = (xmax - xmin) * X + xmin
Where "x" is the parameter value, xmin is the parameter minimum, xmax is the parameter maximum, and X is the standard uniform value.
Converting LHS output from Standard Normal to Parameter Spacex = Z * σx + μx
Where "x" is the parameter value, σx is the parameter standard deviation, μx is the parameter mean value, and Z is the standard normal value.
# Script for generating standard uniform/standard normal
Latin-Hypercube samples
# Parameter space is mapped to an array index space
using integer truncation
# Once array space is filled, a random value is
generated within each cell
# Array space is filled using strata index exclusion
'''
Copyright (c) 2017 Justin M. Hughes
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person
obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation
files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without
restriction, including without limitation the rights to use,
copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or
sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the
Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following
conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT
HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING
FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR
OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
'''
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random,sys,os
from copy import deepcopy
import scipy.stats as st
def getIndex(val,h,minVal=0.0,maxVal=1.0):
minIndex = int(float(minVal/h))
valIndex = int(float(val/h))-minIndex
return valIndex
def indexToEdge(dim,lEdge,h,minVal=0.0,maxVal=1.0):
rEdge = deepcopy(lEdge)
for i in range(0,len(lEdge)):
for j in range(0,dim):
lEdge[i][j] = getFloatVal(lEdge[i][j],h)
rEdge[i][j] = lEdge[i][j]+h
return lEdge,rEdge
def getFloatVal(index,h,minVal=0.0,maxVal=1.0):
return float(index*h+minVal)
def initializeSpace(dim,numStrata,minVal=0.0,maxVal=1.0,debug='False'):
dimList = []
for i in range(0,dim):
dimList.append(numStrata)
h = float((maxVal-minVal)/(numStrata))
return h,getIndex(maxVal,h)
def buildList(dim,numStrata):
eligibleIndices = []
iList = []
for i in range(0,numStrata):
iList.append(i)
for i in range(0,dim):
eligibleIndices.append(iList)
return eligibleIndices
def getLimitedDraw(dim,eligibleIndices,history):
# set eligible indices for each dimension
indices = deepcopy(eligibleIndices)
for ent in history:
for i in range(0,dim):
indices[i] = [x for x in indices[i] if x != ent[i]]
point = []
for i in range(0,dim):
point.append(random.choice(indices[i]))
return point, indices
def getDraw(dim,eligibleIndices,maxIndex,history):
eIndex = deepcopy(eligibleIndices)
#print(len(eIndex[0]))
point = [0]*dim
draws = 0
rejected = 0
invalid = []
while True:
if history == []:
# Initial random draw
point = [np.random.randint(0,maxIndex) for x in point]
history.append(point)
#print(len(history))
break
elif history != []:
# Limited draw by limiting sample-able indices
point,eIndex = getLimitedDraw(dim,eIndex,history)
history.append(point)
#print(len(history))
break
'''
#iterate over each index, compare to history
for ent in history:
for i in range(0,dim):
if point[i] == ent[i]:
invalid.append("True")
else:
invalid.append("False")
if "True" in invalid:
draws += 1
rejected += 1
else:
draws += 1
history.append(point)
break
'''
return list(point),history,eIndex
def convertToRandomCDF(dim,history,h):
#Get bin left edge
leftEdge = deepcopy(history)
rightEdge = deepcopy(history)
#iterate over leftEdge, convert ints to floats
leftEdge, rightEdge = indexToEdge(dim,leftEdge,h)
randCDFVal = deepcopy(leftEdge)
for i in range(0,len(leftEdge)):
for j in range(0,dim):
randCDFVal[i][j] = float(np.random.uniform(leftEdge[i][j],0.999999*rightEdge[i][j],1))
return randCDFVal
def CDFtoNorm(CDF):
dim = len(CDF[0])
CDF = deepcopy(CDF)
for i in range(0,len(CDF)):
for j in range(0,dim):
CDF[i][j] = st.norm.ppf(CDF[i][j])
return CDF
def wtf(data,filename):
f = open(filename,'w')
for ent in data:
for thing in ent:
f.write(str(thing)+',')
f.write('\n')
f.close()
def sample(dim,numSamples,ratio):
numStrata = numSamples
# Try getting different random points in the array space
# to satisfy nearest-neighbor constraint
# In 3 tries, get another LH sample and go again
sampleNum = 0
while True:
history = []
h,maxIndex = initializeSpace(dim,numStrata)
eIndices = buildList(dim,numStrata)
# Maximum radius within a single cell
minRadius = h*np.sqrt(dim)
for i in range(0,numSamples):
point,history,eIndices = getDraw(dim,eIndices,maxIndex,history)
sampleNum += 1
print("Sampling Latin-Hypercube array space (%s)" %(sampleNum))
tries = 0
while True:
randUniform = convertToRandomCDF(dim,history,h)
randStandardNorm = CDFtoNorm(randUniform)
tries += 1
wtf(randUniform,'utemp.csv')
wtf(randStandardNorm,'ntemp.csv')
cols = range(0,dim)
randUniform = np.genfromtxt('utemp.csv',delimiter=',',usecols=cols)
randStandardNorm = np.genfromtxt('ntemp.csv',delimiter=',',usecols=cols)
uninnd = nnd(randUniform)
normnnd = nnd(randStandardNorm)
sampleMin = np.nanmin(uninnd)
sampleMinNorm = np.nanmin(normnnd)
print(sampleMin,sampleMinNorm,ratio*minRadius)
if tries == 3:
break
if sampleMin > ratio*minRadius and sampleMinNorm > ratio*minRadius:
break
if sampleMin > ratio*minRadius and sampleMinNorm > ratio*minRadius:
break
os.remove(os.getcwd()+'/utemp.csv')
os.remove(os.getcwd()+'/ntemp.csv')
return randUniform,randStandardNorm
def nnd(a):
# For each sample, get the nearest neighbor w.r.t. each variable
b = np.zeros((a.shape[0],a.shape[0]),dtype=float)
for i in range(0,b.shape[0]):
for j in range(0,b.shape[0]):
b[i,j] = radius(a[j,:] - a[i,:])
if i == j:
b[i,j] = 10e3
return b
def radius(v):
a = np.nansum(v*v)
return np.sqrt(a)
def help():
# Displays help in terminal
print("\n\tPython script for generating Latin Hypercube samples")
print("\nUsage:\n\t\tpython lhs.py dimensions samples cellRatio\n")
print("\tdimensions: number of dimensions in hypercube")
print("\tsamples: number of samples per dimension")
print("\tcellRatio: ratio of the cell maximum radius for")
print("\t nearest-neighbor limit (default=1.0)")
print("\t Higher ratios force more a space-filling")
print("\t sample, higher chance of no solution")
print("\n\tOutputs: Uniform.csv, StandardNormal.csv")
print("\n\tConvert uniform values to variable values")
print("\t\tvar = range*value + min")
print("\n\tConvert standard normal values to variable values")
print("\t\tvar = stdev*value + mean")
sys.exit("\nHelp called, exiting...")
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
if str(sys.argv[1]) == '-help' or str(sys.argv[1]) == '-h':
help()
except IndexError:
help()
try:
dim = int(sys.argv[1])
except:
dim = 2
try:
numSamples = int(sys.argv[2])
except:
numSamples = 10
try:
minRatio = float(sys.argv[3])
except:
minRatio = 1.0
# Get standard normal and standard uniform samples
uni,std = sample(dim,numSamples,minRatio)
np.savetxt('StandardUniform.csv',uni,delimiter=',')
np.savetxt('StandardNormal.csv',std,delimiter=',')
if dim == 2:
h = 1.0/numSamples
for i in range(1,numSamples):
plt.plot((0,1),(i*h,i*h),'k--',linewidth=1)
plt.plot((i*h,i*h),(0,1),'k--',linewidth=1)
plt.plot(uni[:,0],uni[:,1],'ro')
plt.axes().set_aspect('equal')
plt.xlabel('X',fontsize=18)
plt.ylabel('Y',fontsize=18)
plt.xlim(0,1)
plt.ylim(0,1)
plt.savefig("LHS_2D_example")
plt.clf()
