Corvette C6 Engine Cradle
Made from Magnesium
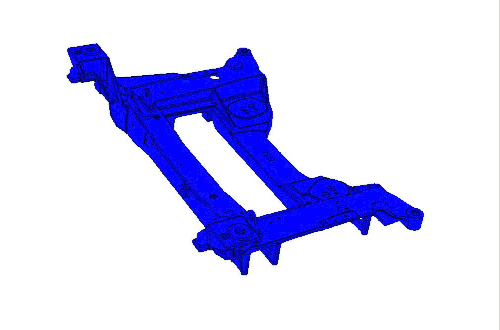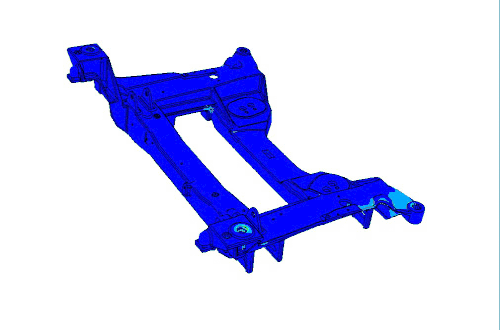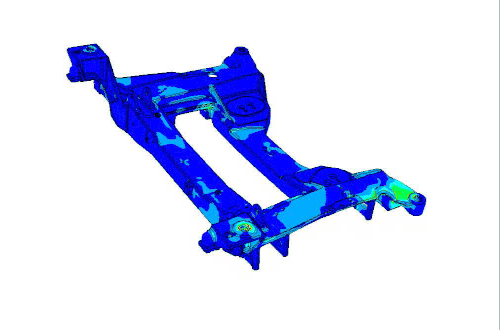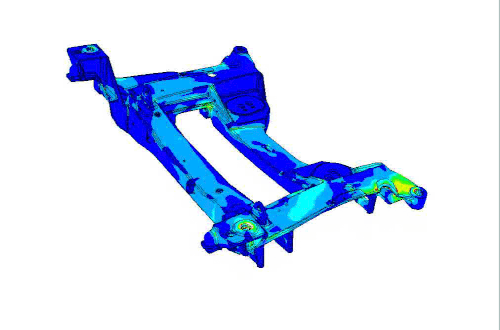
CAVS researchers combine tangible experimentation with modeling to develop next-level materials, like the Corvette Cradle.
Motivated to address the demand of today’s cars – including increased gas mileage, reduced emissions and a reduced need for foreign oil, Dr. Mark Horstemeyer developed the C6 Corvette Cradle.
Beginning with the smallest element of the project, he began investigating the makeup for the cradle. Ultimately, instead of incorporating steel like a traditional cradle design would, Horstemeyer utilized a special magnesium alloy.
The result of his innovative material choice?
The C6 model is 66% lighter than Corvette's C5 model
In comparison to aluminum, titanium and steel, the magnesium alloy has a greater strength per unit volume and is able to withstand much more vibration and stress during use. The innovative engine cradle research was sponsored by the Department of Energy and later incorporated in Corvette models during 2006-2014
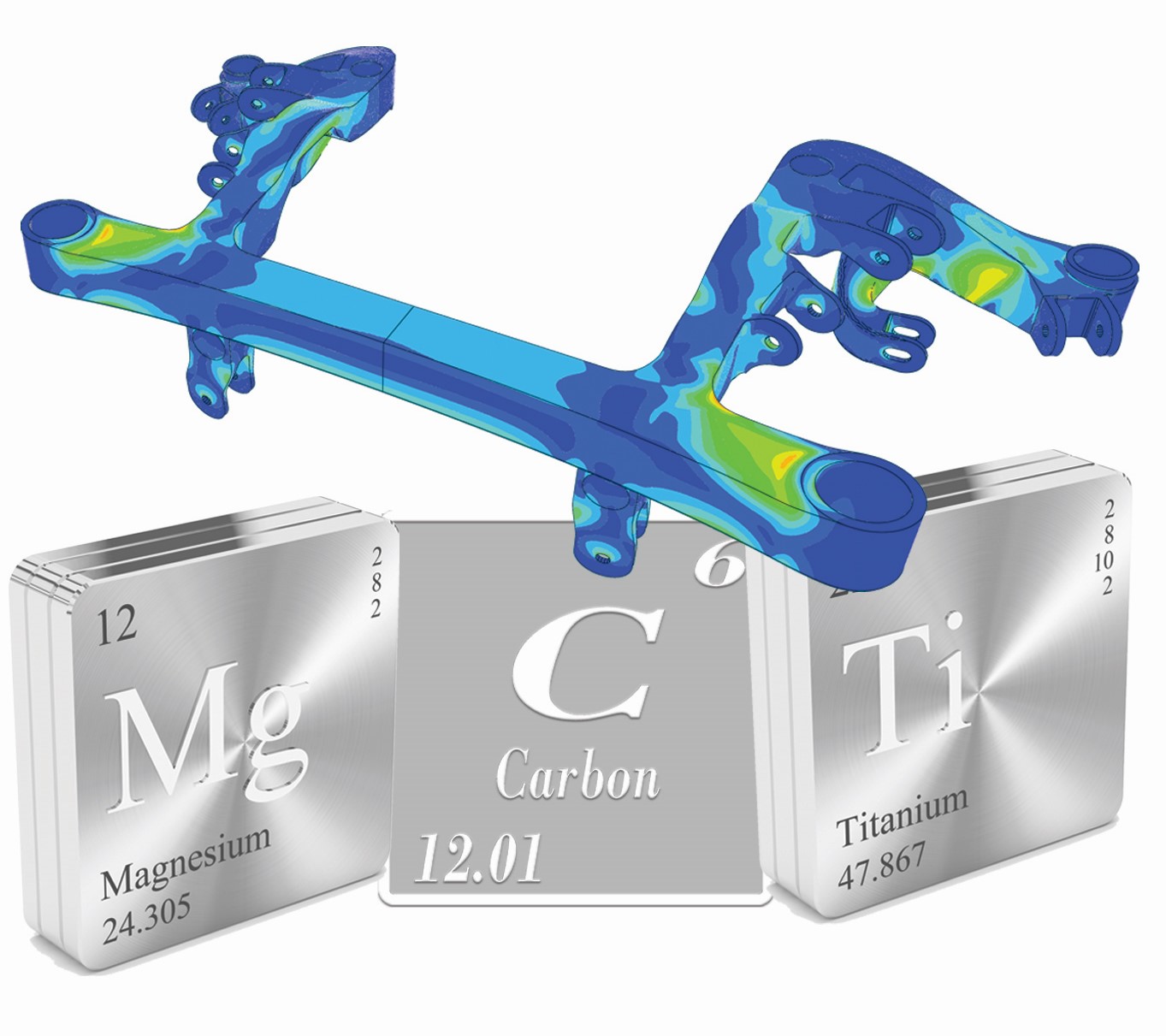
Components of the magnesium alloy subframe
