Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME)
LAMMPS Polymer
Abstract
In this tutorial Molecular dynamics simulation in LAMMPS is used to show what happens to a polymer chain at a certain temperature after some time. Chain's movement is caused by a molecular forces between atoms in the chain and by temperature of the chain. This factors are modeled in LAMMPS in order to show the behavior of this polymer chain. The chain was previously prepared in MATLAB. It contains 100 atoms with bound between neighbor atoms. During the simulation, firstly, the chain was left for do deform freely under the molecular forces and a random atomic fluctuation due to the temperature. After that the chain was minimized to find it's minimal energy condition. The tutorial explains basic LAMMPS commands and shows how to make a movie using AtomEye and ImageJ.
Author(s): Dmitry I. Zhuk, Mark A. Tschopp
Corresponding Author: Mark Tschopp
Input File
The polymer chain of 100 atoms was specially prepared in MATLAB. The atom's Z coordinate does not varies much, all of them are within 2 Å. The distance between atoms is about 1.5 Å. Basically, the chain goes from left upper to right lower corner of the box. At the right you can see the picture of the initial condition of the chain.
The data file is shown below and available for download here: PE_cl100.txt
# Model for PE
100 atoms
99 bonds
98 angles
97 dihedrals
1 atom types
1 bond types
1 angle types
1 dihedral types
0.0000 158.5000 xlo xhi
0.0000 158.5000 ylo yhi
0.0000 100.0000 zlo zhi
Masses
1 14.02
Atoms
1 1 1 5.6240 5.3279 51.6059
2 1 1 7.4995 7.4810 50.2541
3 1 1 8.2322 8.0236 51.2149
4 1 1 9.6108 9.9075 51.7682
5 1 1 11.5481 11.3690 50.4167
6 1 1 12.9409 13.4562 50.2481
7 1 1 14.4708 14.8569 50.0868
8 1 1 16.1916 16.4790 50.5665
9 1 1 17.1338 17.6853 51.8189
10 1 1 19.1109 19.4000 50.3869
...
Bonds
1 1 1 2
2 1 2 3
3 1 3 4
4 1 4 5
5 1 5 6
6 1 6 7
7 1 7 8
8 1 8 9
9 1 9 10
10 1 10 11
...
Angles
1 1 1 2 3
2 1 2 3 4
3 1 3 4 5
4 1 4 5 6
5 1 5 6 7
6 1 6 7 8
7 1 7 8 9
8 1 8 9 10
...
Dihedrals
1 1 1 2 3 4
2 1 2 3 4 5
3 1 3 4 5 6
4 1 4 5 6 7
5 1 5 6 7 8
6 1 6 7 8 9
7 1 7 8 9 10
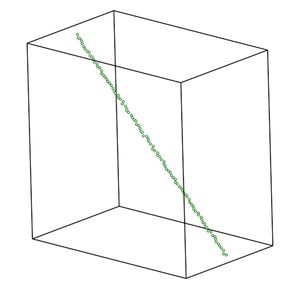
Figure 1. Not-deformed polymer chain.
Here, the first section defines the numbers of atoms, bonds, angles and dihedrals. Lower you can see the types and the box sizes. Below that are the simulation box sizes.
Then comes the Atoms section. The first column is the atom number, then comes the atom type and some other information not used in this tutorial. Last three columns is the atom's x, y and z coordinates correspondingly.
In the Angle section listed the angles between atoms. First column is the angle number, second - angle ID, then comes the atom's number between which the angle is defined. Example of the distribution of the atoms can be seen on Figure 2. Dihedrals are a little bit more complicated. To define a diherdal four atoms are needed. Syntax are pretty much similar to the angles section. The only difference is that one more atom is needed to define a dihedral. Basically, the dihedral angle is the angle between the planes formed by 2 groups of 3 neighbor atoms. You see the example on Figure 3.
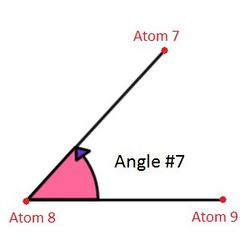
Figure 2. Angles between atoms defined in LAMMPS.
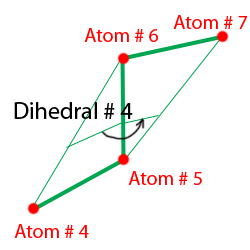
Figure 3. Angles between atoms defined in LAMMPS.
LAMMPS Script
Below is the script used for the actual simulation. This input script was run using the Aug 2015 version of LAMMPS. Changes in some commands in more recent versions may require revision of the input script. This script runs the simulation with the previously discussed data file.
#####################################################
# #
# #
# Filename: in.deform.polychain.txt #
# Author: Mark Tschopp, 2010 #
# #
# The methodology outlined here follows that from #
# Hossain, Tschopp, et al. 2010, Polymer. Please #
# cite accordingly. The following script requires #
# a LAMMPS data file containing the coordinates and #
# appropriate bond/angle/dihedral lists for each #
# united atom. #
# #
# Execute the script through: #
# lmp_exe < in.deform.polychain.txt #
# #
#####################################################
# VARIABLES
variable fname index PE_cl100.txt
variable simname index PE_cl100
# Initialization
units real
boundary f f f
atom_style molecular
log log.${simname}.txt
read_data ${fname}
# Dreiding potential information
neighbor 0.4 bin
neigh_modify every 10 one 10000
bond_style harmonic
bond_coeff 1 350 1.53
angle_style harmonic
angle_coeff 1 60 109.5
dihedral_style multi/harmonic
dihedral_coeff 1 1.73 -4.49 0.776 6.99 0.0
pair_style lj/cut 10.5
pair_coeff 1 1 0.112 4.01 10.5
compute csym all centro/atom fcc
compute peratom all pe/atom
#####################################################
# Equilibration (Langevin dynamics at 5000 K)
velocity all create 5000.0 1231
fix 1 all nve/limit 0.05
fix 2 all langevin 5000.0 5000.0 10.0 904297
thermo_style custom step temp
thermo 10000
timestep 1
run 1000000
unfix 1
unfix 2
write_restart restart.${simname}.dreiding1
#####################################################
# Define Settings
compute eng all pe/atom
compute eatoms all reduce sum c_eng
#####################################################
# Minimization
dump 1 all cfg 6 dump.comp_*.cfg mass type xs ys zs c_csym c_peratom fx fy fz
reset_timestep 0
fix 1 all nvt temp 500.0 500.0 100.0
thermo 20
thermo_style custom step pe lx ly lz press pxx pyy pzz c_eatoms
min_style cg
minimize 1e-25 1e-25 500000 1000000
print "All done"
In general, this script does equilibration and minimization to the polymer chain. Polymer chain data file named 'PE_cl100.txt' should be the same directory. Line "dump 1 all cfg 6 dum..." used to output information during simulation can be moved before the equilibration part of the script to output the process of equilibration. Please note that you need to change a time step for a dump command otherwise it will give too many or very few dump files. It may be reasonable to choose a timestep of 10,000 for equilibration and 6 for minimization. That will give about 100 files for each step.
# VARIABLES
variable fname index PE_cl100.txt
variable simname index PE_cl100
# Initialization
units real
boundary f f f
atom_style molecular
log log.${simname}.txt
read_data ${fname}
This part is just opens the data file, defines the boundary conditions, units, logfile's name, etc.
# Dreiding potential information neighbor 0.4 bin neigh_modify every 10 one 10000 bond_style harmonic bond_coeff 1 350 1.53 angle_style harmonic angle_coeff 1 60 109.5 dihedral_style multi/harmonic dihedral_coeff 1 1.73 -4.49 0.776 6.99 0.0 pair_style lj/cut 10.5 pair_coeff 1 1 0.112 4.01 10.5
In this section goes the information about the bonds, angles, dihedrals in a chain. Bond_style and bond_coeff defines the type on the force field between atoms and a magnitude of this fields. "1" here corresponds to the second column of the "Bonds" section of the data file. Thus, every atom pair with "1" in the second column will be having such properties during the simulation. Similar goes to the angles and dihedrals. Angle_* and dihedral_* lines defines the angles and dihedral angles between atoms in the polymer chain. Pair_* commands used to define pair potentials between atoms that are within a cutoff distance. More about this commands and a parameters can be found at SANDIA website: https://lammps.sandia.gov/doc/Section_commands.html#cmd_5
compute csym all centro/atom fcc compute peratom all pe/atom
his commands are used to define which properties are to be calculated during the simulation. For example, "pe/atom" simply means to calculate the potential energy for each atom. Information about other possible properties to calculate can be found here.
# Equilibration (Langevin dynamics at 5000 K)
velocity all create 5000.0 1231
fix 1 all nve/limit 0.05
fix 2 all langevin 5000.0 5000.0 10.0 904297
thermo_style custom step temp
thermo 10000
timestep 1
run 1000000
unfix 1
unfix 2
write_restart restart.${simname}.dreiding1
The equilibration step allows the chain to deform freely under the temperature driven movements of the atoms. Velocity command add the temperature to the chain. Fix command performs the check of the system every time step and updates the velocity and positions of the atoms. Thermo commands defines thermo output during the simulation. Run command stars the dynamic transformation.
##################################################### # Minimization dump 1 all cfg 6 dump.comp_*.cfg id type xs ys zs c_csym c_peratom fx fy fz reset_timestep 0 fix 1 all nvt temp 500.0 500.0 100.0 thermo 20 thermo_style custom step pe lx ly lz press pxx pyy pzz c_eatoms min_style cg minimize 1e-25 1e-25 500000 1000000
The other step in the program is the minimization. It finds the minimum energy condition for such configuration. The parameters for minimize command includes: stopping tolerance for energy, stopping tolerance for force, max iterations of minimizer and max number of force/energy evaluations. Where stopping tolerance for energy being the first parameter and the max number of force/energy evaluations the last one.
LAMMPS Logfile
Here is the logfile produced by LAMMPS during the simulation. Note that the temperature during the equilibration does not concave and just randomly changes over time. On the other hand, the potential energy during the minimization lowers over time until it reaches the minimum for this configuration within a tolerance.
read_data ${fname}
read_data PE_cl100.txt
1 = max bonds/atom
1 = max angles/atom
1 = max dihedrals/atom
orthogonal box = (0 0 0) to (158.5 158.5 100)
2 by 2 by 1 processor grid
100 atoms
99 bonds
98 angles
97 dihedrals
2 = max # of 1-2 neighbors
2 = max # of 1-3 neighbors
4 = max # of 1-4 neighbors
6 = max # of special neighbors
# Dreiding potential information
neighbor 0.4 bin
neigh_modify every 10 one 10000
bond_style harmonic
bond_coeff 1 350 1.53
angle_style harmonic
angle_coeff 1 60 109.5
dihedral_style multi/harmonic
dihedral_coeff 1 1.73 -4.49 0.776 6.99 0.0
pair_style lj/cut 10.5
pair_coeff 1 1 0.112 4.01 10.5
compute csym all centro/atom fcc
compute peratom all pe/atom
#####################################################
# Equilibration (Langevin dynamics at 5000 K)
velocity all create 5000.0 1231
fix 1 all nve/limit 0.05
fix 2 all langevin 5000.0 5000.0 10.0 904297
thermo_style custom step temp
thermo 10000
timestep 1
run 1000000
Memory usage per processor = 5.96847 Mbytes
Step Temp
0 5000
10000 4503.8382
20000 4389.5108
30000 4137.4417
40000 5341.7194
50000 4458.9062
60000 5377.3337
70000 5004.3444
80000 4338.4843
90000 4691.7776
100000 4733.5682
110000 4701.5107
120000 4855.5683
130000 4477.8402
140000 4538.7404
150000 4588.4541
160000 4862.2936
170000 4684.8557
180000 4485.3563
190000 4759.6888
200000 5381.965
210000 5137.9384
220000 4812.9015
230000 4628.1747
240000 4645.6596
250000 4913.3042
260000 5404.8637
270000 4420.5497
280000 5357.551
290000 5009.1386
300000 4610.7359
310000 4752.3123
320000 4358.3474
330000 4961.3549
340000 4317.1413
350000 4154.0022
360000 5339.4602
370000 4460.511
380000 4997.8213
390000 4354.7411
400000 4797.0648
410000 4830.892
420000 5087.6876
430000 4723.8778
440000 4629.8021
450000 4976.1032
460000 4609.4548
470000 5019.8023
480000 4446.1004
490000 4862.2646
500000 5026.155
510000 4431.281
520000 4391.5373
530000 4214.6362
540000 4846.1485
550000 4807.4181
560000 4488.3661
570000 5360.1736
580000 5071.4535
590000 4463.498
600000 4555.1718
610000 5114.4069
620000 4699.2292
630000 5142.6987
640000 4479.5147
650000 4671.0304
660000 4564.5161
670000 4265.3884
680000 4814.3015
690000 4964.3923
700000 5121.2814
710000 5230.1069
720000 4297.1403
730000 4433.7983
740000 5176.7691
750000 4783.2431
760000 4792.0254
770000 4318.1008
780000 5279.5916
790000 4970.3985
800000 4163.3936
810000 5014.5128
820000 4423.9304
830000 4860.6778
840000 4502.2809
850000 4738.7186
860000 4585.4628
870000 4851.0205
880000 4747.5203
890000 4511.0158
900000 4841.8463
910000 5075.7912
920000 5070.3709
930000 4343.2652
940000 4743.7859
950000 4020.8883
960000 4671.5891
970000 4446.4685
980000 4448.264
990000 4507.5559
1000000 4873.6706
Loop time of 36.1922 on 4 procs for 1000000 steps with 100 atoms
Pair time (%) = 4.03491 (11.1486)
Bond time (%) = 8.30473 (22.9462)
Neigh time (%) = 1.95553 (5.40319)
Comm time (%) = 19.297 (53.3182)
Outpt time (%) = 0.00102639 (0.00283595)
Other time (%) = 2.59897 (7.18103)
Nlocal: 25 ave 39 max 5 min
Histogram: 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1
Nghost: 45.75 ave 62 max 25 min
Histogram: 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1
Neighs: 267.75 ave 425 max 44 min
Histogram: 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1
FullNghs: 0 ave 0 max 0 min
Histogram: 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Total # of neighbors = 1071
Ave neighs/atom = 10.71
Ave special neighs/atom = 5.88
Neighbor list builds = 100000
Dangerous builds = 100000
unfix 1
unfix 2
write_restart restart.${simname}.dreiding1
write_restart restart.PE_cl100.dreiding1
#####################################################
# Define Settings
compute eng all pe/atom
compute eatoms all reduce sum c_eng
#####################################################
# Minimization
dump 1 all cfg 6 dump.comp_*.cfg id type xs ys zs c_csym c_peratom fx fy fz
reset_timestep 0
fix 1 all nvt temp 500.0 500.0 100.0
thermo 20
thermo_style custom step pe lx ly lz press pxx pyy pzz c_eatoms
min_style cg
minimize 1e-25 1e-25 500000 1000000
WARNING: Resetting reneighboring criteria during minimization
Memory usage per processor = 6.81045 Mbytes
Step PotEng Lx Ly Lz Press Pxx Pyy Pzz eatoms
0 1237.2398 158.5 158.5 100 16.181003 10.716166 11.032966 26.793875 1237.2398
20 93.175603 158.5 158.5 100 23.387346 19.859621 23.64755 26.654868 93.175603
40 63.587362 158.5 158.5 100 25.830375 21.672133 27.047328 28.771665 63.587362
60 54.741088 158.5 158.5 100 26.066912 21.364531 27.7035 29.132705 54.741088
80 48.917554 158.5 158.5 100 25.87727 20.908929 27.620402 29.102479 48.917554
100 45.293817 158.5 158.5 100 26.386696 21.757562 27.905252 29.497275 45.293817
120 41.459225 158.5 158.5 100 25.974718 20.775913 27.911315 29.236928 41.459225
140 37.876111 158.5 158.5 100 25.799883 20.794051 27.553625 29.051972 37.876111
160 36.701952 158.5 158.5 100 25.852641 20.951326 27.544375 29.062221 36.701952
180 35.07739 158.5 158.5 100 26.004914 21.057098 27.774282 29.183362 35.07739
200 33.877666 158.5 158.5 100 25.961315 21.11421 27.590146 29.17959 33.877666
220 31.12208 158.5 158.5 100 23.995326 19.308908 24.96515 27.711921 31.12208
240 28.809216 158.5 158.5 100 25.831303 21.277521 27.270668 28.945719 28.809216
260 26.02543 158.5 158.5 100 25.951859 21.58113 27.157947 29.116498 26.02543
280 23.070199 158.5 158.5 100 26.005868 21.781819 27.222861 29.012922 23.070199
300 20.013665 158.5 158.5 100 25.453848 20.749404 26.676606 28.935533 20.013665
320 18.738385 158.5 158.5 100 25.954677 21.603359 27.136183 29.124488 18.738385
340 16.749844 158.5 158.5 100 25.789221 21.322696 27.03715 29.007817 16.749844
360 15.8834 158.5 158.5 100 25.985101 21.659604 27.170167 29.125532 15.8834
380 14.987185 158.5 158.5 100 25.977784 21.397522 27.357437 29.178393 14.987185
400 14.517165 158.5 158.5 100 25.95897 21.55348 27.296561 29.026868 14.517165
420 13.7945 158.5 158.5 100 26.006995 21.535186 27.281645 29.204153 13.7945
440 12.512098 158.5 158.5 100 25.840513 21.28497 27.217437 29.019132 12.512098
460 12.290892 158.5 158.5 100 25.924928 21.357401 27.298119 29.119263 12.290892
480 10.775174 158.5 158.5 100 25.830121 21.201044 27.158886 29.130434 10.775174
500 10.218356 158.5 158.5 100 25.614842 21.0218 26.893606 28.92912 10.218356
520 9.8614258 158.5 158.5 100 25.93082 21.345743 27.320707 29.126011 9.8614258
540 9.1390877 158.5 158.5 100 25.893538 21.32844 27.283388 29.068787 9.1390877
560 8.5527184 158.5 158.5 100 25.954932 21.387239 27.355923 29.121632 8.5527184
580 8.1607915 158.5 158.5 100 25.865475 21.24017 27.270322 29.085934 8.1607915
600 7.8012324 158.5 158.5 100 25.950545 21.404499 27.375776 29.071362 7.8012324
620 7.6152706 158.5 158.5 100 25.937275 21.370367 27.342438 29.099019 7.6152706
640 7.3593621 158.5 158.5 100 25.940706 21.344493 27.415647 29.061979 7.3593621
656 7.2144567 158.5 158.5 100 25.915345 21.326291 27.308608 29.111136 7.2144567
Loop time of 0.712466 on 4 procs for 656 steps with 100 atoms
Minimization stats:
Stopping criterion = linesearch alpha is zero
Energy initial, next-to-last, final =
1237.23980569 7.21445672663 7.21445672663
Force two-norm initial, final = 1373.33 1.10527
Force max component initial, final = 285.91 0.235955
Final line search alpha, max atom move = 6.31527e-09 1.49012e-09
Iterations, force evaluations = 656 3308
Pair time (%) = 0.0280486 (3.93683)
Bond time (%) = 0.0298776 (4.19355)
Neigh time (%) = 0.00120121 (0.168599)
Comm time (%) = 0.05711 (8.01581)
Outpt time (%) = 0.359286 (50.4284)
Other time (%) = 0.236944 (33.2568)
Nlocal: 25 ave 41 max 4 min
Histogram: 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1
Nghost: 47.25 ave 65 max 26 min
Histogram: 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
Neighs: 287.25 ave 507 max 30 min
Histogram: 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
FullNghs: 573 ave 992 max 47 min
Histogram: 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
Total # of neighbors = 2292
Ave neighs/atom = 22.92
Ave special neighs/atom = 5.88
Neighbor list builds = 51
Dangerous builds = 0
print "All done"
All done
LAMMPS dump files
Also, the dump files have been produced during the simulation. The can be used to produce a movie.
Movie
- Go to AtomEye website.
- Click on Download, this will take you to the raw binary files.
- Download the A.i686 version by right-clicking on the link and "Save Target As..." to one of your directories.
- Rename the downloaded file as A by typing "cp A.i686 A". A will be the executable.
- Using UNIX, run "chmod A 755" on the file to change this to an executable.
- To test, you need to save a CFG file as well, such as cnt8x3.cfg. Try running using "./A cnt8x3.cfg".
- Go to ImageJ website.
- Download the appropriate version for Windows, LINUX, or MAC
- Visualize the dumpfile in AtomEye by typing the following command, "/A dump.tensile_0.cfg" (UNIX).
- Visualize the dumpfile in AtomEye by typing the following command, "/A dump.tensile_0.cfg" (UNIX).
- Use Alt+0 to activate centrosymmetric (csym) view.
- Adjust threshold, or set of atoms to view, by using Shift+T. This will allow creation of a set for the current parameter (in this case, csym). Please note that you need to adjust both lower and higher thresholds unless the atoms from following images that exceeds maximum value for the first one will be not shown. You can make it 5 or 10.
- Make atoms with values outside of the threshold invisible by using Ctrl+A.
- Press 'y' within AtomEye to produce an animation script.
- The folder "Jpg" now contains snapshots of all dumpfiles.
- Open ImageJ
- Drag the folder Jpg into ImageJ
- Select "Convert to RGB" to keep the color from the AtomEye images.
- Choose "yes" to load a stack.
- Adjust the size as needed (Image/Adjust/Size)
- Adjust frame rate as desired (Image/Stacks/Tools/Animation Options)
- Save as Animated Gif file
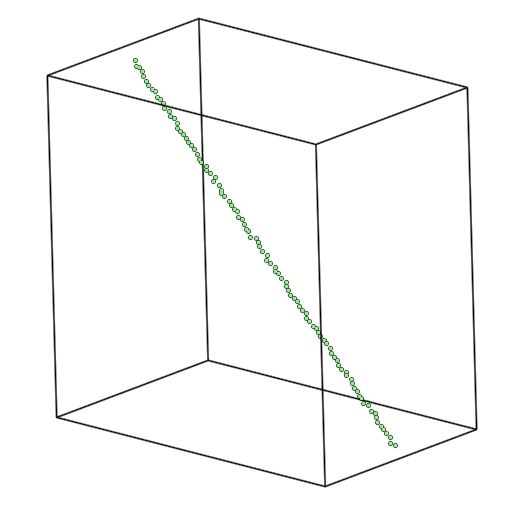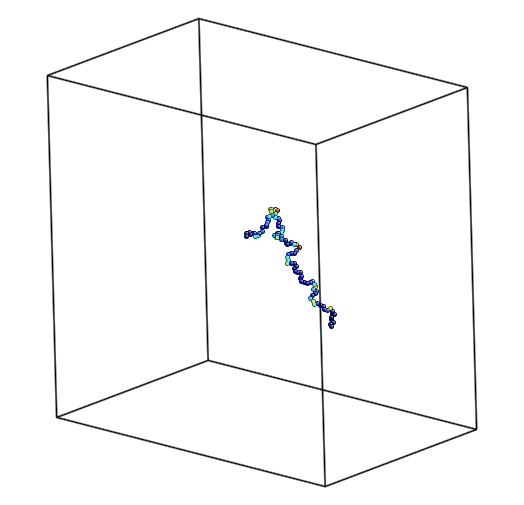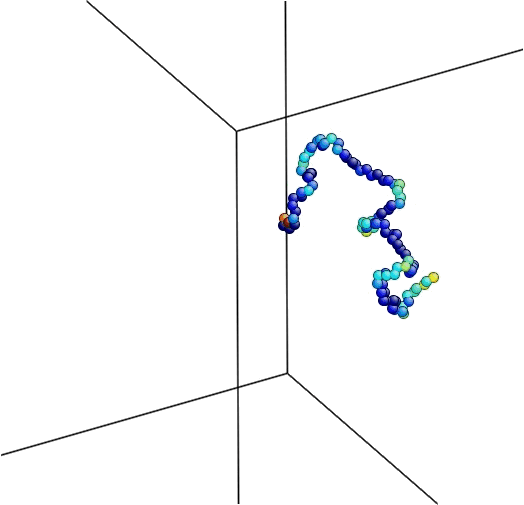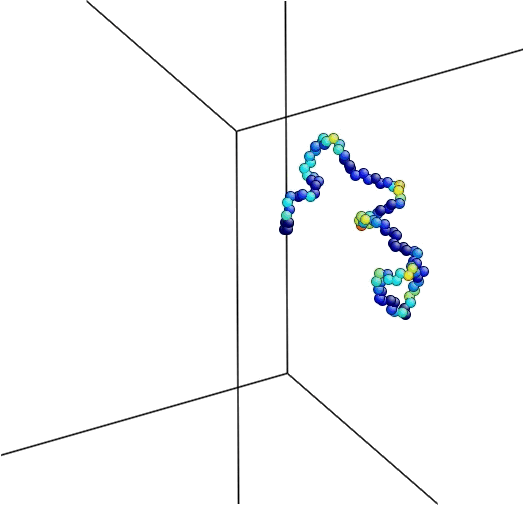
Figure 4. The equilibration process followed by minimization.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge funding for this work through the Department of Energy.
